TCP three-Way Handshake
| Step | Direction | What’s Sent | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| SYN | Client → Server | I want to connect, here’s my sequence number | Tells the server: I want to connect, get ready. |
| SYN+ACK | Server → Client | I accept, here’s my sequence number, and I got yours | Server says: OK, I’m ready too, and I received your request. |
| ACK | Client → Server | I received your sequence number | Client confirms: Got it, we’re both ready, let’s communicate. |
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) includes the standard TCP three-way handshake as part of its connection process.
After the TCP connection is established, HTTPS initiates a TLS handshake to provide encryption and secure communication.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) also uses the TCP three-way handshake, but does not include any encryption.
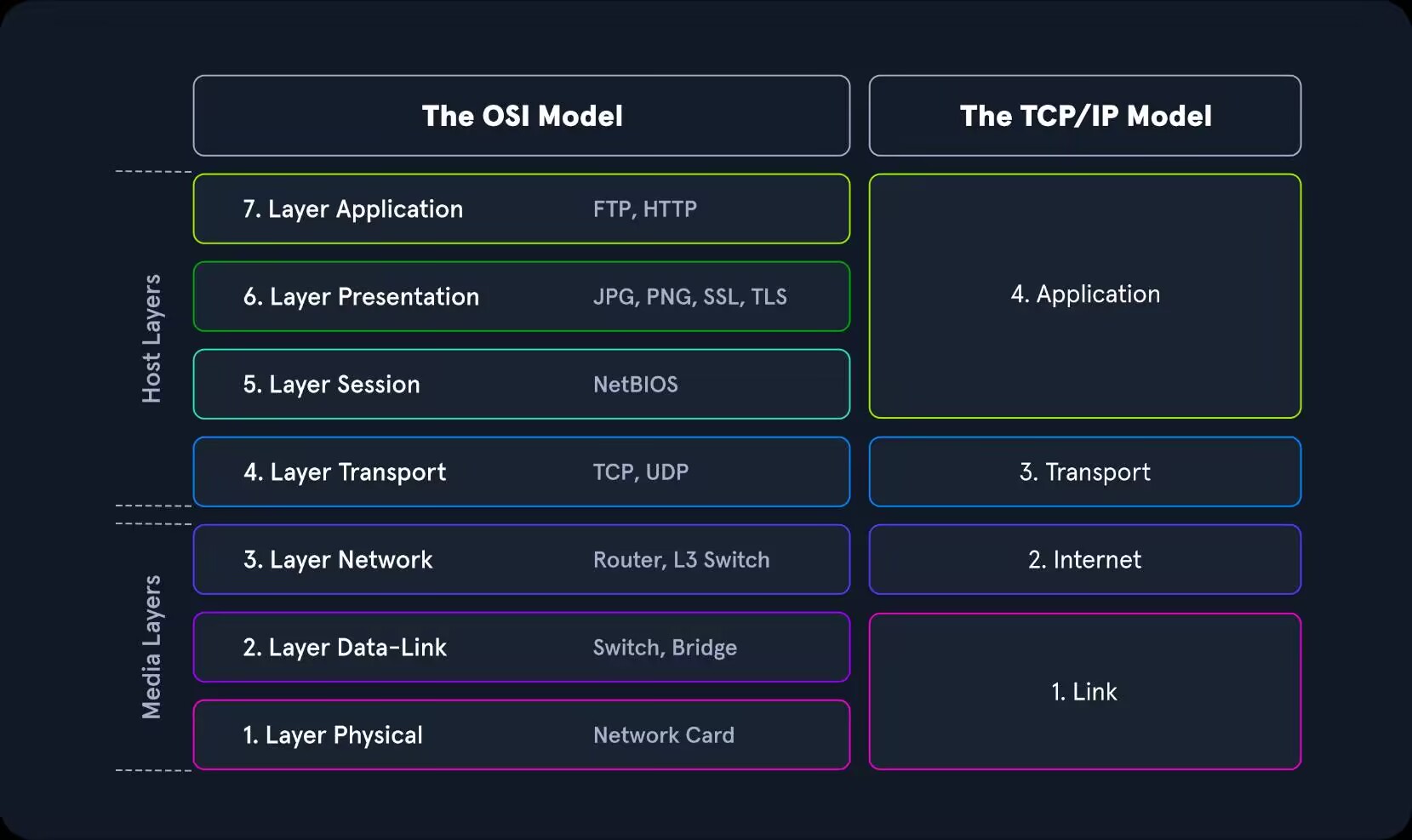
|Layer 1 | Physical | Cables,fiber,signcal itself|
|Layer 2 | Bata Link | Frame,MAC address,Extended Unique Identifier(EUI-48,EUI-64),Switch |
|Layer 3 | Network | IP Address,Router,Packet|
|Layer 4 | Transport | TCP segement,UDP datagram|
|Layer 5 | Session | Control protocols ,tunneling protocols|
|Layer 6 | Presentation | Application encryption (SSL/TLS)|
|Layer 7 | Appication | eyes|
|CDN| Content Delivery Network|
|VPN| Virtual Private Network|
|QoS| Quality of Service|
|TTL| Time to live|
|IP | Internet Protocol|
|NFV| Network function virtualization|
|Routing loops| tracert 10.4.10.1|
|DNS| Domain Name System| dig www.google.com|
Designing the cloud
Virtual Network